Top 10 Signs it’s Time to Focus on Application Modernization
What is application modernization? In this article, learn what application modernization is and how it can impact your business.
What is application modernization? In this article, learn what application modernization is and how it can impact your business.
What is Application Modernization? Application modernization is the process of updating or transforming existing software applications to leverage the latest technologies, architectures, and best practices. It aims to improve the performance, functionality, scalability, security, and user experience of legacy applications while ensuring they remain relevant in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape. To put it simply, it is the software development equivalent of renovating an older home to take advantage of improvements to efficiency, safety, structural integrity and so forth.
Why modernize legacy applications? Application modernization enables an organization to protect its investments and refresh its software portfolio to take advantage of contemporary infrastructure, tools, languages, and other technology progress. A robust application modernization strategy can reduce the resources required to run an application, increase the frequency and reliability of deployments, and improve uptime and resiliency, among other benefits. As a result, an application modernization plan is a common feature of an enterprise’s overall digital transformation strategy.
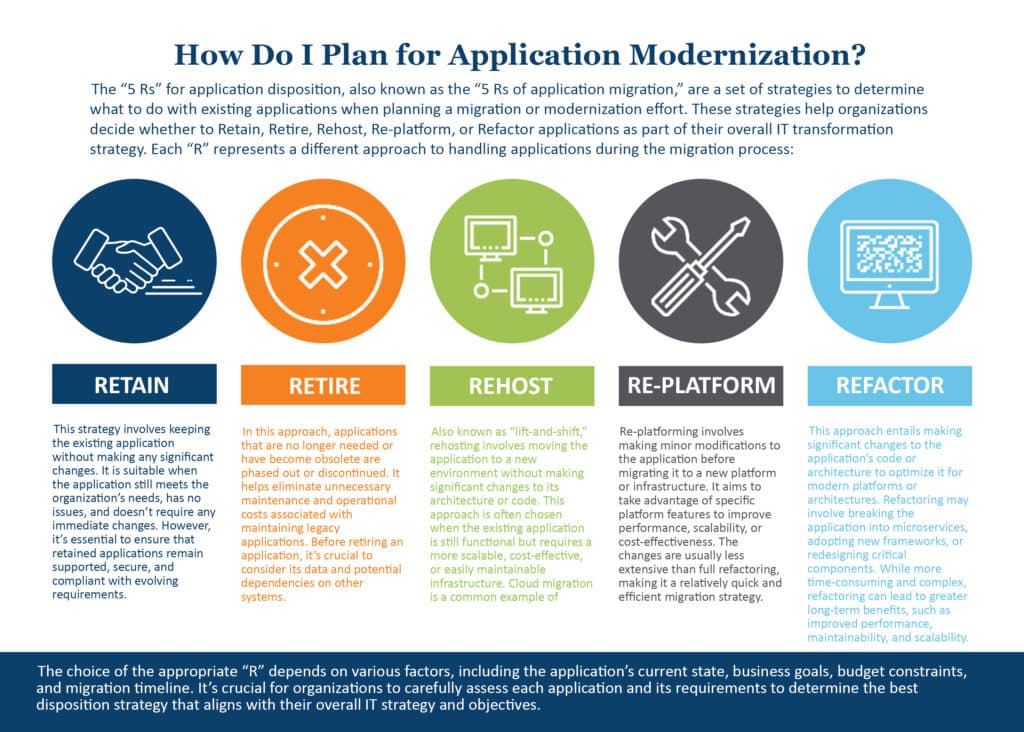
The “5 Rs” for application disposition, also known as the “5 Rs” of application migration,” are a set of strategies to determine what to do with existing applications when planning a migration or modernization effort. These strategies help organizations decide whether to Retain, Retire, Rehost, Re-platform, or Refactor applications as part of their overall IT transformation strategy. Each “R” represents a different approach to handling applications during the migration process:
Retain: This strategy involves keeping the existing application without making any significant changes. It is suitable when the application still meets the organization’s needs, has no issues, and doesn’t require any immediate changes. However, it’s essential to ensure that retained applications remain supported, secure, and compliant with evolving requirements.
Retire: In this approach, applications that are no longer needed or have become obsolete are phased out or discontinued. It helps eliminate unnecessary maintenance and operational costs associated with maintaining legacy applications. Before retiring an application, it’s crucial to consider its data and potential dependencies on other systems.
Rehost: Also known as “lift-and-shift,” rehosting involves moving the application to a new environment without making significant changes to its architecture or code. This approach is often chosen when the existing application is still functional but requires a more scalable, cost-effective, or easily maintainable infrastructure. Cloud migration is a common example of rehosting.
Re-platform: Re-platforming involves making minor modifications to the application before migrating it to a new platform or infrastructure. It aims to take advantage of specific platform features to improve performance, scalability, or cost-effectiveness. The changes are usually less extensive than full refactoring, making it a relatively quick and efficient migration strategy.
Refactor: This approach entails making significant changes to the application’s code or architecture to optimize it for modern platforms or architectures. Refactoring may involve breaking the application into microservices, adopting new frameworks, or redesigning critical components. While more time-consuming and complex, refactoring can lead to greater long-term benefits, such as improved performance, maintainability, and scalability.
The choice of the appropriate “R” depends on various factors, including the application’s current state, business goals, budget constraints, and migration timeline. It’s crucial for organizations to carefully assess each application and its requirements to determine the best disposition strategy that aligns with their overall IT strategy and objectives.
If you identify one or more of these signs in your critical business applications, it’s a strong indication that it’s time to consider modernizing your systems to enhance productivity, user experience, and overall business performance.
Velosio has helped thousands of organizations with modernization strategies, including system replacement, cloud migration, and application rearchitecting. By recognizing the signs of the need for modernization, organizations can proactively address issues and take advantage of the benefits it offers.
Let us know how we can help your organization today with application modernization.
Talk to us about how Velosio can help you realize business value faster with end-to-end solutions and cloud services.